PALI-2108
Precision Medicine Approach to
Ulcerative Colitis (UC) and Fibrostenotic Crohn’s Disease (FSCD)
PALI-2108: PDE4 Inhibitor Prodrug That Acts Locally at Site of Disease
Patients with Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis (UC) and Fibrostenotic Crohn’s Disease (FSCD) Overexpress PDE4 and Related Biomarkers
Elevated PDE4B Expression:
Our bioinformatics and machine learning research has identified a measurable threshold of elevated PDE4B expression across more than 1,600 patients and 10 studies, enabling the identification of over-expressing patients in over 70% of cases. This robust finding supports the potential for an FDA-approved test that uses PDE4B expression as a reliable marker for patient enrichment. In both ulcerative colitis (UC) and fibrostenotic Crohn’s disease (FSCD), higher PDE4B expression is linked to local inflammatory activity. By targeting these pathways, our PDE4 prodrug therapeutic aims to deliver higher local PDE4 inhibitor levels, maximizing efficacy while minimizing systemic exposure.
Elevated PDE4B-Related Biomarkers:
Using advanced machine learning techniques, we have also developed a second approach featuring six PDE4B-related biomarkers. This test has demonstrated superior performance over benchmark diagnostics and is specifically optimized for PDE4 inhibition. Tailored for both UC and FSCD, it offers a precision solution to enhance therapeutic outcomes. The integration of PCR-based assays aimed at potential FDA approval will ensure accuracy in patient targeting. These developments reflect the Company’s dedication to advancing precision medicines across inflammatory bowel diseases, including UC and FSCD, and to transforming the standard of care through targeted, personalized treatment strategies.
PALI-2108 Highlights
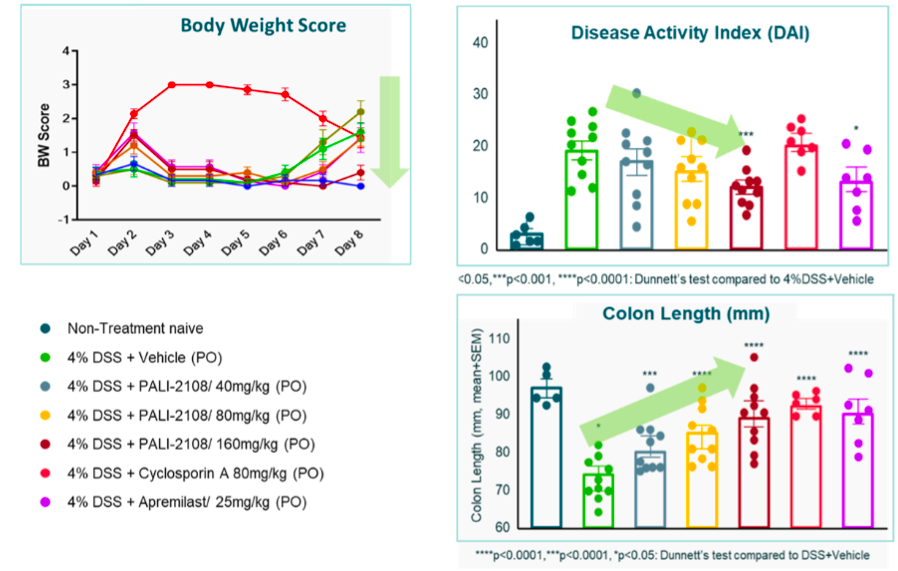
Demonstrated Improved Efficacy Over Standard of Care and Systemic PDE4 Inhibitors in DSS Colitis Mouse Model
PALI-2108 demonstrated clear dose dependent improvements in clinical outcome measures and was better than SOC in DSS colitis mouse model.
While apremilast showed efficacy, it was at a dose not well tolerated when translated to human, including nausea.*
Danse et al. evaluated 60mg and 80mg daily doses in UC patients which is ~1mg/kg; whereas we used the HED of ~2mg/kg in this study.
*Danse et al
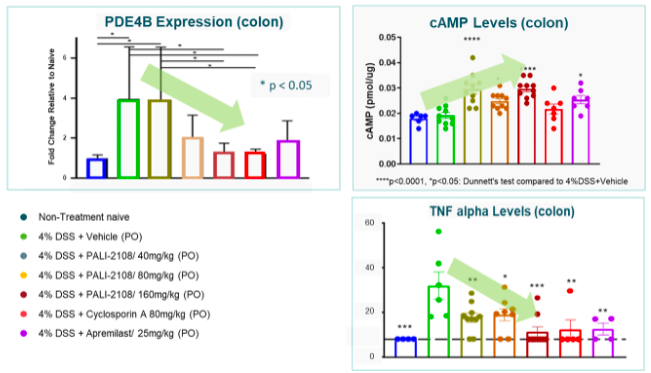
Colon tissue PDE4B Expression (mRNA) was reduced in response to PALI-2108 in a dose dependent manner together with local PDE4B inhibition and increased intracellular cAMP.
cAMP levels were increased more with PALI-2108 and TNF-alpha levels in colon tissue are normalized on average in most animals.
Significant Unmet Need in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Chronic condition characterized by persistant inflammation in the digestive tract in early adulthood with alternating periods of activity and remission.
Only 30-40% of Patients Fail to Respond to First-Line Therapy1
Market Expected to Grow to $20B by 20312
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a group of chronic, immune-mediated conditions that cause persistent inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, primarily including Ulcerative Colitis (UC) and Fibrostenotic Crohn’s Disease (FSCD). UC involves continuous inflammation and ulceration of the colon and rectum, leading to symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and rectal bleeding. FSCD, a complication of Crohn’s Disease, is characterized by chronic inflammation and fibrosis that narrows the intestines, causing obstructive symptoms like cramping and bloating. Together, these conditions highlight the need for precision therapies that address both inflammatory and fibrotic pathways in IBD.
Current IBD Market3,4
Ulcerative Colitis
1.95 Millon Cases
$7.7 Billion Market
Crohn’s Disease
1.63 Millon Cases
$8 Billion Market
- Kappelman MD, Moore KR, Allen JK, Cook SF. Recent trends in the prevalence of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis in a commercially insured US population NIH external link. Digestive Diseases and Sciences. 2013;58(2):519–525. doi:10.1007/s10620-012-2371-5
- Global Data
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- United European Gastroenterology
PDE4 Platform
Precision Medicine Approach
Sign Up For Alerts