Precision Medicine
Our Innovative Precision Medicine Approach: Leveraging Machine Learning to Predict Patient Responders
Targeting Patients with Elevated PDE4 Activity (PDE4 Related Biomarkers)
To predict and effectively treat patients most likely to benefit from specific therapies, our precision medicine platform integrates advanced machine learning with comprehensive patient data analysis. We start by curating and normalizing a large database that includes detailed disease status and severity information, alongside normal controls. This data is used to identify key biomarkers through the use of RNA sequencing and meta-analysis, focusing on PDE4-effector genes. By leveraging systems biology, we confirm these biomarkers as critical drivers of disease pathology. Machine learning then refines the selection of biomarkers, assessing their impact on disease activity and severity, and optimizes the number of key biomarkers needed to accurately predict patient responses to PDE4 inhibitors. This approach ensures targeted and effective treatments, enhancing the likelihood of positive patient outcomes and remission. As part of our ongoing work towards a precision medicine test to identify patients likely to respond to PALI-2108, RNAseq datasets were analyzed using a standardized bioinformatics pipeline, which generates normalized TPM counts for each gene. The analysis found that PDE4B expression is significantly higher in most colitis patients, encompassing both adult and pediatric cohorts. This suggests that PDE4B could be a crucial factor in patient stratification. In adults, a PDE4B over-expression level was determined that the Company believes accurately identifies 70% of moderate to severe cases. In pediatric patients, a PDE4B over-expression level was determined that the Company believes accurately identifies 90% of those with moderate to severe colitis.
We have used well accepted preclinical models to confirm this approach. We have demonstrated increased colon tissue PDE4B levels with induction of colitis and significant reductions in colon tissue PDE4B expression in response to increasing doses of PALI-2108 in an accepted mouse model of colitis. We also demonstrated, closely correlated and increasing levels of colon tissue cAMP, and closely correlated to colon tissue inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha. We additionally observed a significant reduction in disease activity index score over time compared to the control treated group. Further, body weight loss and changes in colon length were attenuated in increasing dosage groups, showcasing the potential for targeted efficacy.
Our Innovative Precision Medicine Approach: Leveraging Machine Learning to Predict Patient Responders
Targeting Patients with Elevated PDE4 Activity (PDE4 Related Biomarkers)
To predict and effectively treat patients most likely to benefit from specific therapies, our precision medicine platform integrates advanced machine learning with comprehensive patient data analysis. We start by curating and normalizing a large database that includes detailed disease status and severity information, alongside normal controls. This data is used to identify key biomarkers through the use of RNA sequencing and meta-analysis, focusing on PDE4-effector genes. By leveraging systems biology, we confirm these biomarkers as critical drivers of disease pathology. Machine learning then refines the selection of biomarkers, assessing their impact on disease activity and severity, and optimizes the number of key biomarkers needed to accurately predict patient responses to PDE4 inhibitors. This approach ensures targeted and effective treatments, enhancing the likelihood of positive patient outcomes and remission. As part of our ongoing work towards a precision medicine test to identify patients likely to respond to PALI-2108, RNAseq datasets were analyzed using a standardized bioinformatics pipeline, which generates normalized TPM counts for each gene. The analysis found that PDE4B expression is significantly higher in most colitis patients, encompassing both adult and pediatric cohorts. This suggests that PDE4B could be a crucial factor in patient stratification. In adults, a PDE4B over-expression level was determined that the Company believes accurately identifies 70% of moderate to severe cases. In pediatric patients, a PDE4B over-expression level was determined that the Company believes accurately identifies 90% of those with moderate to severe colitis.
We have used well accepted preclinical models to confirm this approach. We have demonstrated increased colon tissue PDE4B levels with induction of colitis and significant reductions in colon tissue PDE4B expression in response to increasing doses of PALI-2108 in an accepted mouse model of colitis. We also demonstrated, closely correlated and increasing levels of colon tissue cAMP, and closely correlated to colon tissue inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha. We additionally observed a significant reduction in disease activity index score over time compared to the control treated group. Further, body weight loss and changes in colon length were attenuated in increasing dosage groups, showcasing the potential for targeted efficacy.
Process
Identify Markers of Colitis
RNAseq DiffExp
Top Ranked Genes (U or D)
Top Ranked in Multiple Studies
Relation with PDE4
- Identify Markers of Colitis
- RNAseq DiffExp
- Top Ranked Genes (U or D)
- Top Ranked in Multiple Studies
- Relation with PDE4
Output
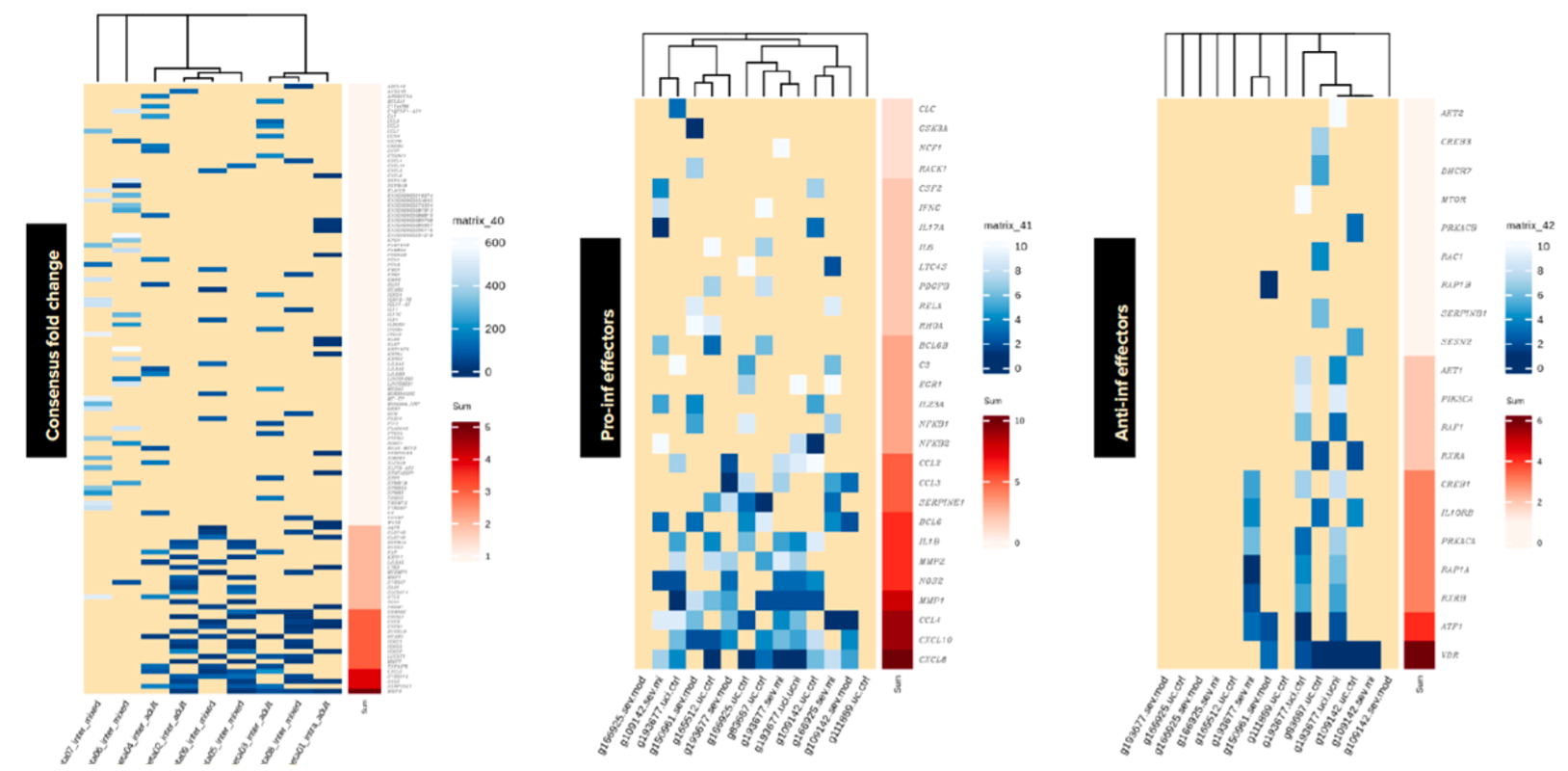
- Identified PDE4-effector genes predictive of patient response to PDE4 inhibitors using advanced bioinformatics tools.
- Selected key drivers of disease pathology for moderately to severely active UC patients through systems biology and machine learning.
- Ranked genes by their importance using meta-analysis, focusing on both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory markers.
- Generated a weighted Disease Activity Score (DAS) for precise patient stratification and treatment targeting.
Meta-Analysis
PDE4B-Based Selection Alone Could Be a Breakthrough for UC Treatment
Elevated PDE4B Expression
Our bioinformatics and machine learning research has identified a measurable threshold of elevated PDE4B expression across more than 1,600 patients and 10 studies, enabling the identification of over-expressing patients in over 70% of cases. This robust finding supports the potential for an FDA-approved test that uses PDE4B expression as a reliable marker for patient enrichment. In addition to higher local PDE4 inhibitor levels, this will maximize the efficacy of our UC PDE4 prodrug therapeutic.
Elevated PDE4B-Related Biomarkers
Using advanced machine learning techniques we have advanced a second approach featuring six PDE4B-related biomarkers. This test has shown superior performance compared to benchmark tests and is specifically tailored for PDE4 inhibition, providing a targeted solution for enhancing therapeutic outcomes. The integration of PCR-based assays aimed at potential FDA approval will ensure precision in patient targeting. These developments underscore the Company’s commitment to developing new precision medicines for UC, driving forward personalized treatment strategies that aim to transform patient care.
PDE4 Platform
Lead Program: PALI-2108
Sign Up For Alerts
